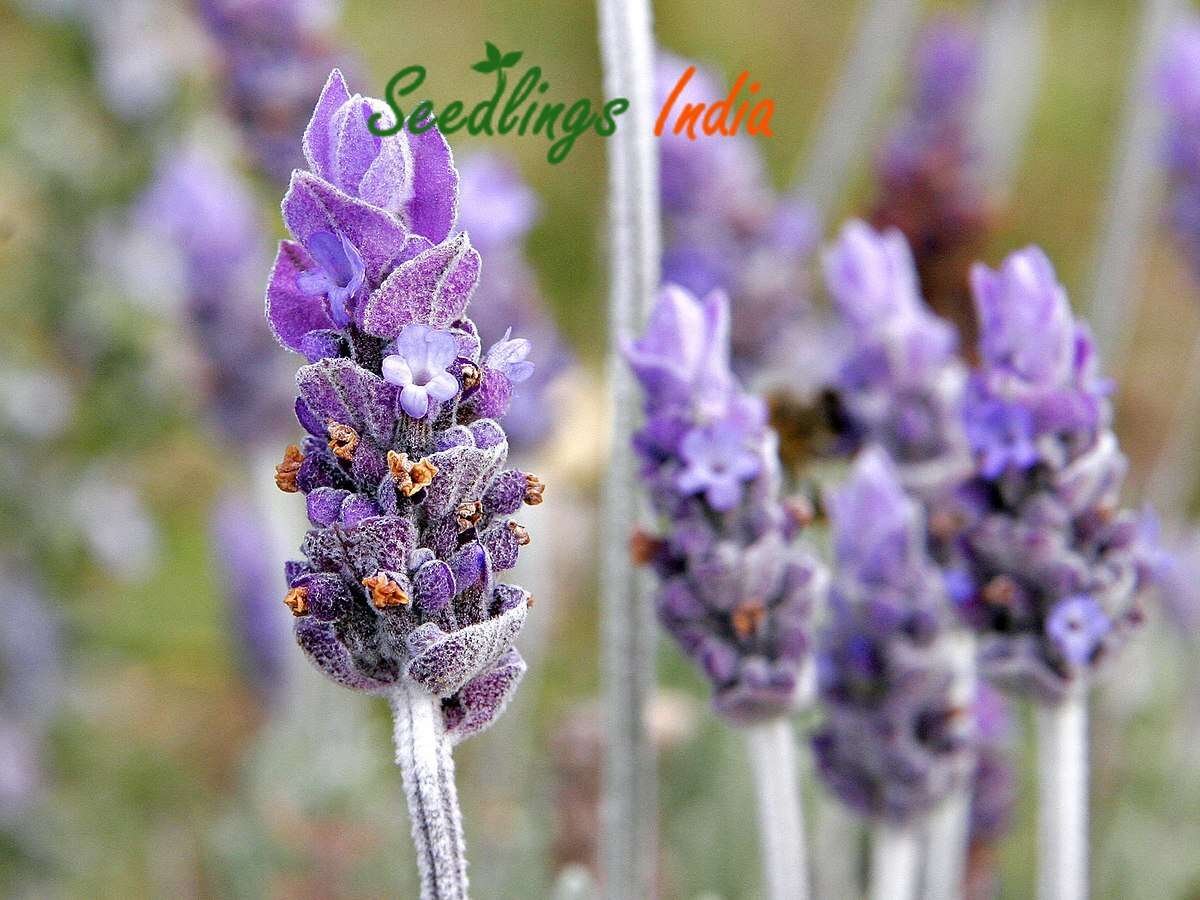
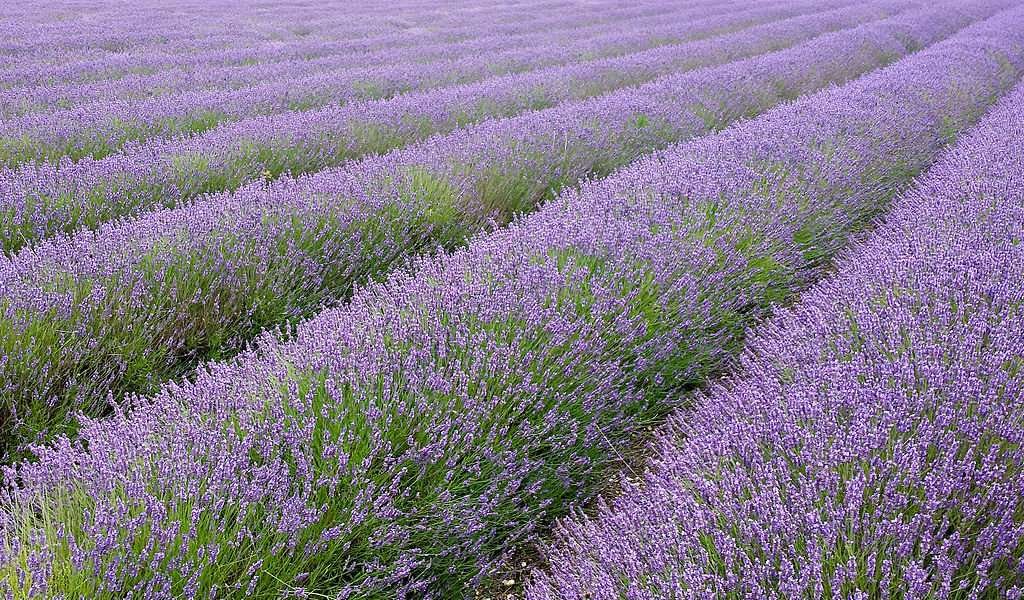
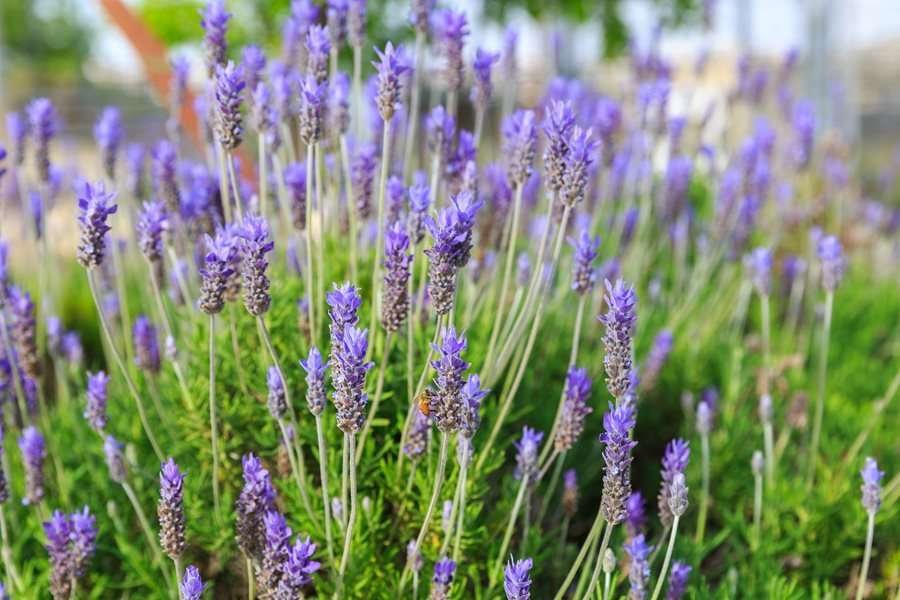
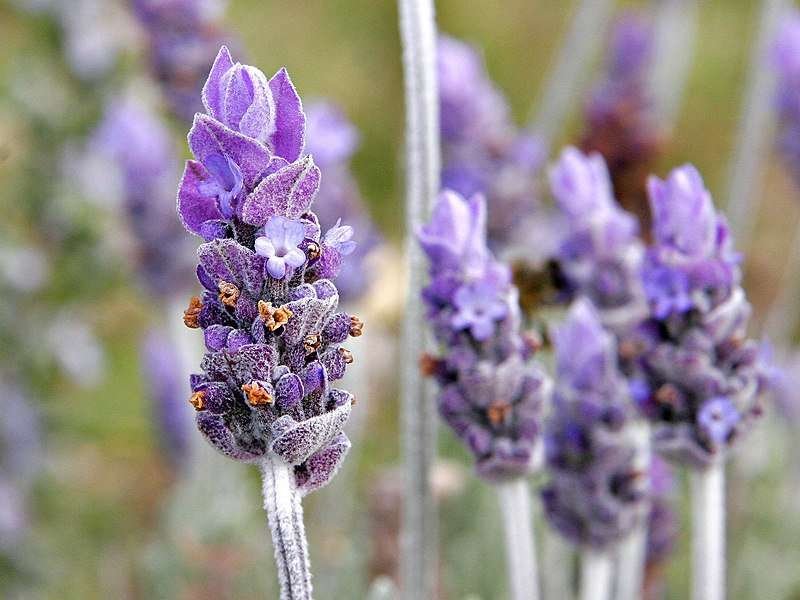
Lavender Herb Seeds
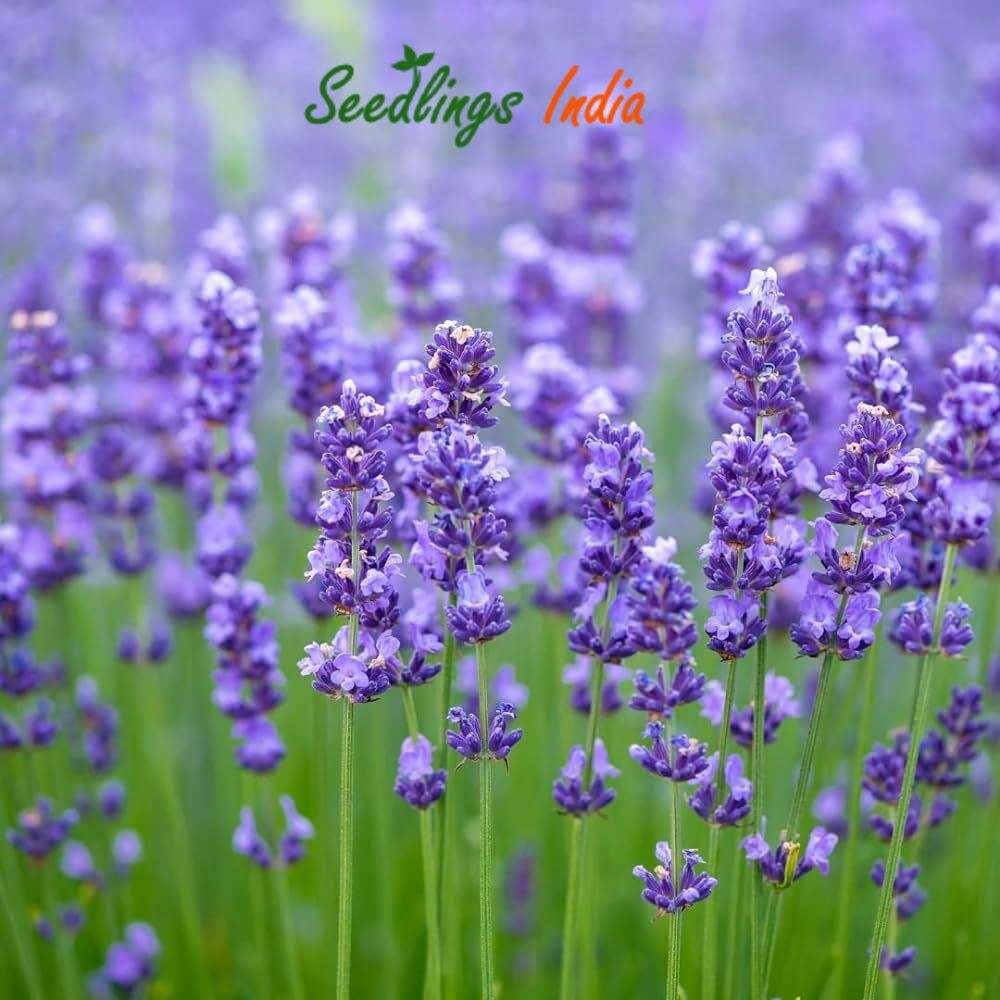
Lavender Herb Seeds (Lavandula angustifolia) is a highly fragrant herb native to the Mediterranean region, well-known for its beautiful purple flowers and calming aroma. It is prized for both its ornamental beauty and its culinary, medicinal, and aromatic uses. Lavender is a versatile herb, often grown in gardens, used in crafts, essential oils, and even cooking. Here’s a detailed guide on Lavender Herb Seeds:
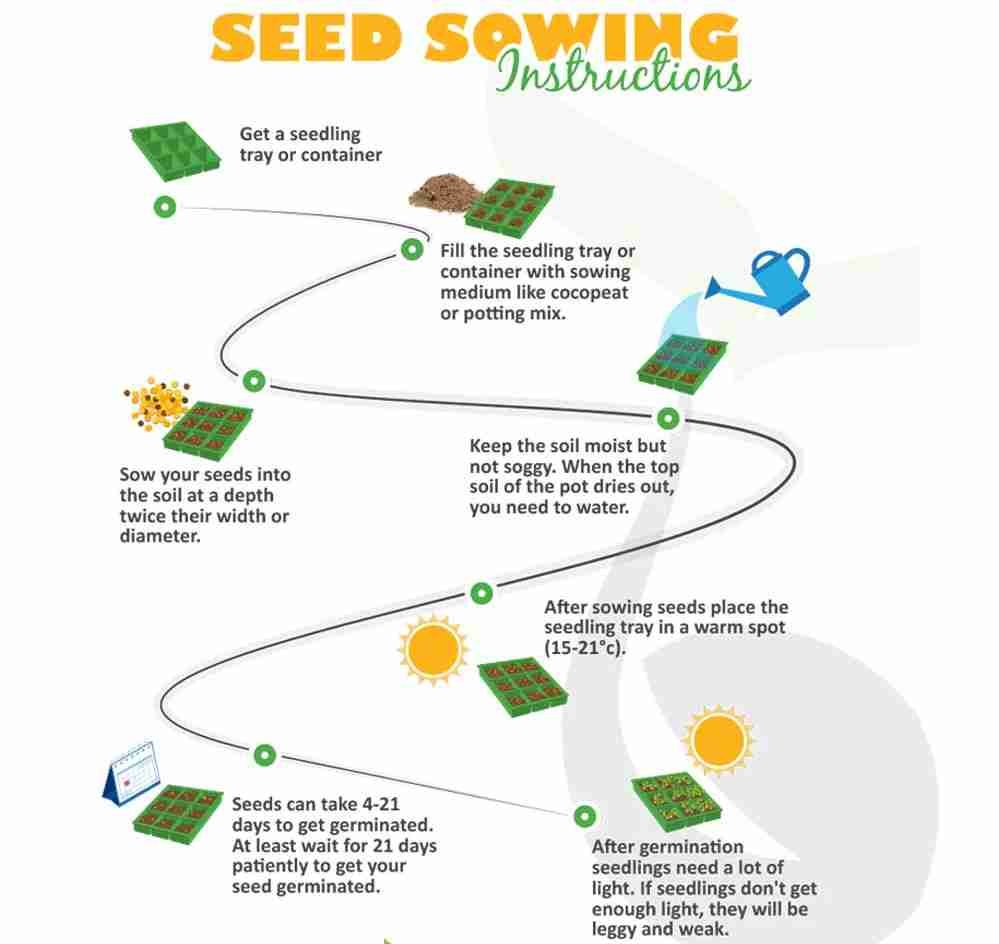
1. Germination and Planting of Lavender Herb Seeds
- Soil: Lavender thrives in well-drained, sandy or loamy soil with a slightly alkaline pH of 6.7–7.3. It does not tolerate heavy, waterlogged soils, so good drainage is essential.
- Sowing Indoors: Lavender seeds can be challenging to germinate, so it’s best to start them indoors 8–10 weeks before the last frost. Stratify the seeds by placing them in the refrigerator for about 2–4 weeks before sowing to improve germination rates.
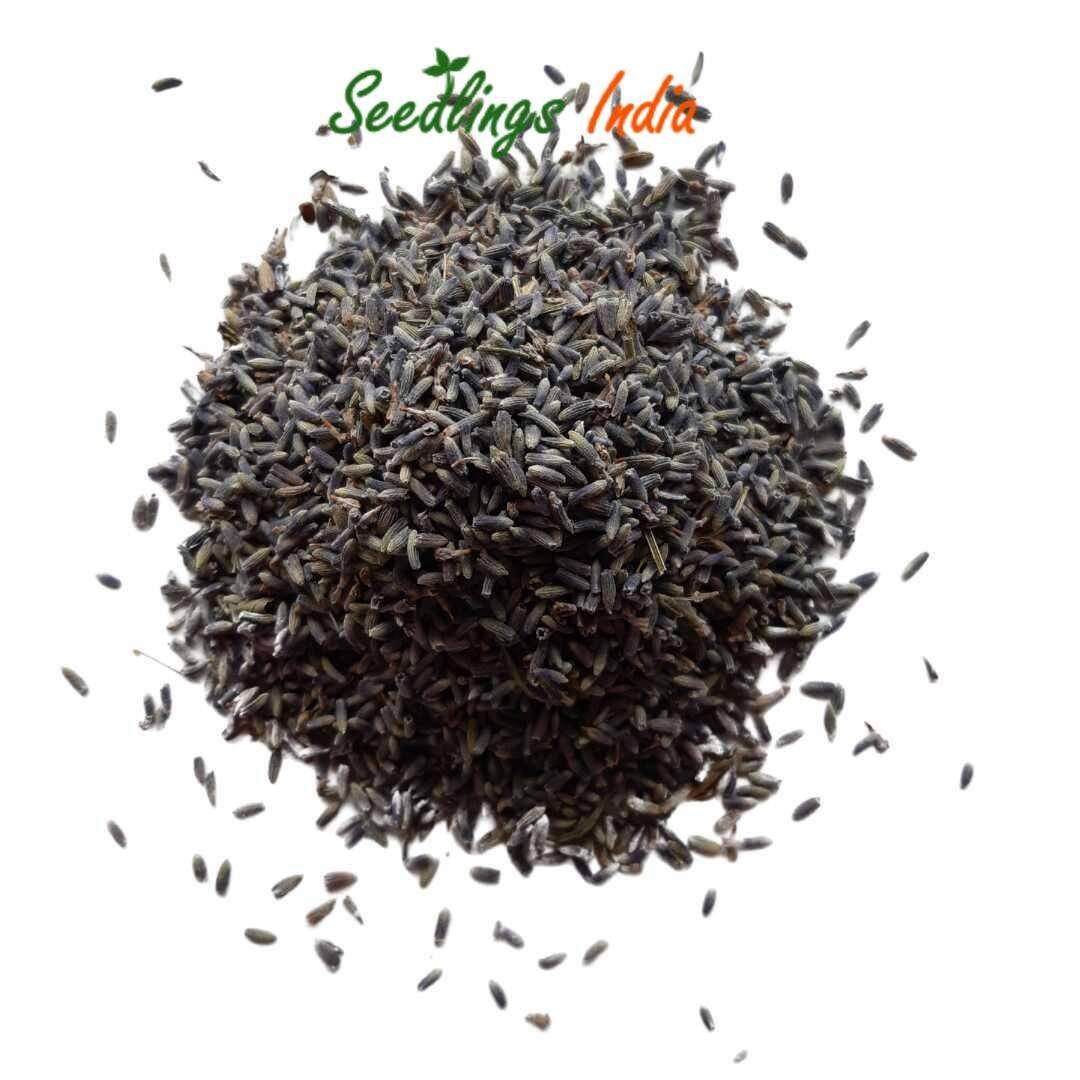
- Planting Depth: Sow the seeds shallowly, about 1/8 inch (3 mm) deep, and cover lightly with soil. Keep the soil moist until germination, which can take 14–28 days.
- Transplanting: After the danger of frost has passed and seedlings have developed several true leaves, they can be transplanted outdoors. Space the plants 12–18 inches apart to allow air circulation.
- Sunlight: Lavender requires full sun, at least 6–8 hours of direct sunlight per day, for optimal growth and flowering.
2. Growth and Care of Lavender Herb Seeds
- Watering: Lavender is drought-tolerant once established and prefers slightly dry conditions. Water young plants regularly until they are established, but avoid overwatering, as this can cause root rot.
- Fertilization: Lavender does not need heavy fertilization. If necessary, use a light application of compost or a low-nitrogen fertilizer in early spring. Too much fertilizer can reduce flower production.
- Pruning: Prune lavender annually in early spring to remove dead wood and shape the plant. This encourages new growth and helps maintain a compact form.
- Temperature: Lavender thrives in warm, dry climates. It is hardy in USDA zones 5–9, though in colder zones it may need winter protection, such as mulching or growing in pots that can be moved indoors during harsh weather.
3. Culinary Uses of Lavender Herb Seeds
- Flavor Profile: Lavender has a sweet, floral taste with hints of mint and rosemary, making it a popular ingredient in both savory and sweet dishes.
- Uses:
- Herbes de Provence: Dried lavender is often included in this classic French herb blend, used in roasted meats and vegetable dishes.
- Desserts: Lavender pairs well with sugar and is often used in cookies, cakes, and ice creams.
- Teas: Lavender flowers can be steeped in hot water to make a soothing herbal tea, often combined with other herbs like chamomile or mint.
- Beverages: Lavender syrup or infused honey is commonly used in cocktails, lemonades, and lattes.
Lavender’s flavor is strong, so use it sparingly to avoid overpowering dishes.
4. Aromatic and Medicinal Uses of Lavender Herb Seeds
- Essential Oils: Lavender oil is one of the most popular essential oils, known for its calming and relaxing properties. It is often used in aromatherapy to reduce stress, anxiety, and insomnia.
- Skincare: Lavender oil and flowers are commonly used in homemade soaps, lotions, and bath products due to their anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties.
- Herbal Remedies: Lavender has been used traditionally to alleviate headaches, promote relaxation, and soothe skin irritations like burns, insect bites, and acne.
- Sachets and Potpourri: Dried lavender flowers are often used in sachets to scent clothing drawers, closets, or rooms, and in potpourri for natural fragrance.
5. HarvestingÂ
- When to Harvest: Lavender flowers should be harvested just before the buds fully open when the color is vibrant, and the scent is strongest. This is usually in late spring or early summer.
6. Growing Lavender Indoors
- Container Gardening: Lavender can be grown indoors in pots, provided it receives plenty of light. Choose a well-draining potting mix and a container with drainage holes to prevent root rot.
- Watering and Care: Allow the soil to dry out slightly between waterings, and avoid overwatering. Turn the pot periodically to ensure even growth.
- Indoor Air Circulation: Lavender grows best in well-ventilated spaces, so ensure proper air circulation indoors to prevent fungal diseases.











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.