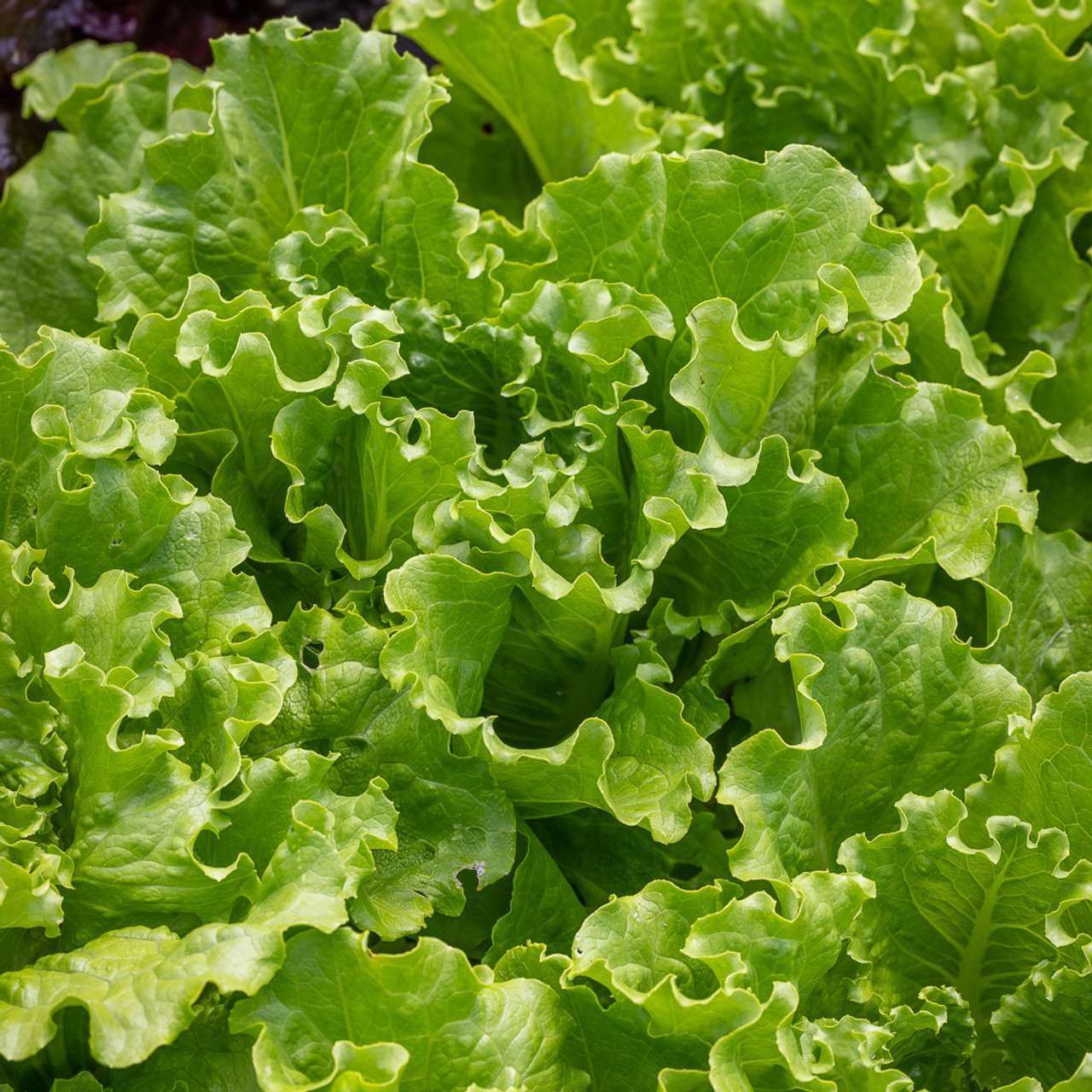
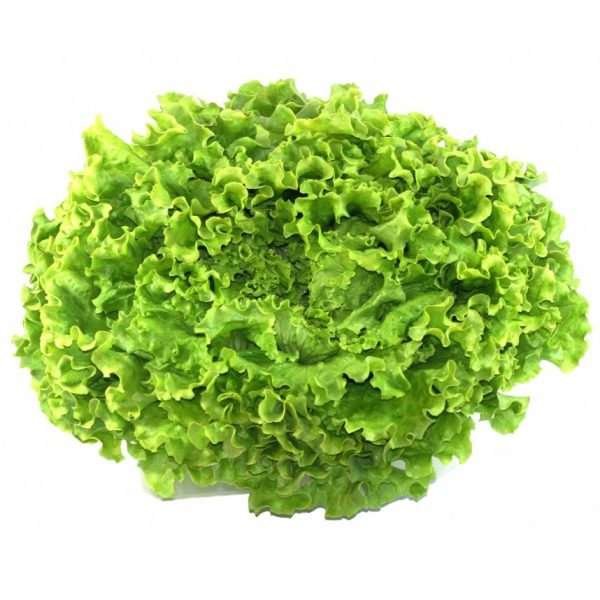
Lettuce Batavia Herb Seeds (Lactuca sativa var. Batavia) is a type of loose-leaf lettuce known for its crisp texture, wavy leaves, and mild flavor. It’s often described as having characteristics between crisphead (iceberg) lettuce and loose-leaf varieties, making it a favorite for both home gardens and gourmet salads. Batavia lettuce comes in green and red varieties, adding diversity and color to dishes.
Here’s a comprehensive guide on Lettuce Batavia Herb Seeds:
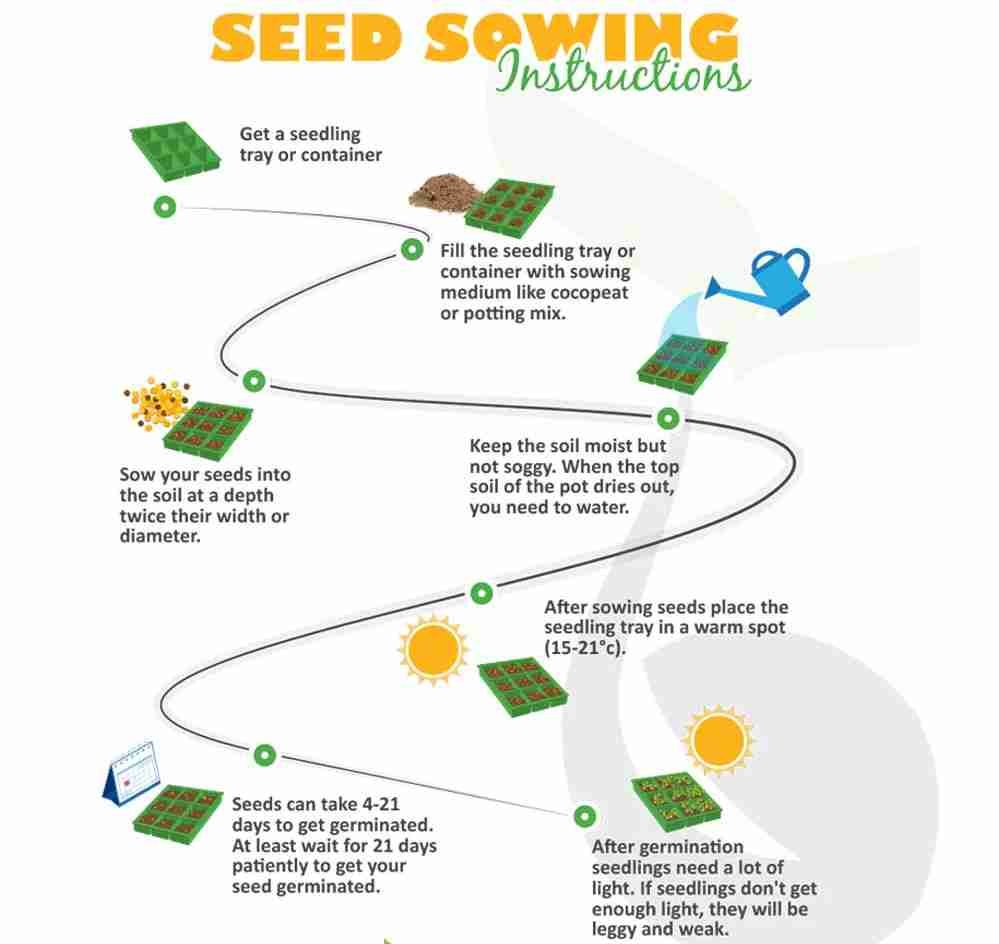
1. Germination and Planting of Lettuce Batavia Herb Seeds
- Soil: Batavia lettuce prefers loose, well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. The ideal pH is between 6.0 and 7.0.
- Sowing: You can either start Batavia lettuce indoors or sow the seeds directly into the garden once the danger of frost has passed. Seeds can also be sown in late summer for a fall crop, as lettuce thrives in cooler weather.
- Planting Depth: Sow seeds shallowly, about 1/4 inch (6 mm) deep. Keep the soil moist until germination, which usually occurs within 7–10 days.
- Spacing: Thin or transplant seedlings to about 8–12 inches apart to allow the leaves to grow fully. For rows, space them about 12–18 inches apart.
- Sunlight: Batavia lettuce grows best in full sun but can tolerate partial shade, especially in warmer climates.
2. Growth and Care of Lettuce Batavia Herb Seeds
- Watering: Lettuce needs consistent moisture to grow well. Keep the soil evenly moist but not waterlogged, as lettuce is sensitive to both drought and overwatering. Mulching around the base of the plants can help retain soil moisture and keep the roots cool.
- Fertilization: Batavia lettuce is a light feeder. Use a balanced organic fertilizer or side-dress with compost during the growing season to provide nutrients. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to bitter-tasting leaves.
- Temperature: Lettuce grows best in cooler temperatures (60–65°F or 15–18°C). In hot weather, it can bolt (go to seed) quickly, so planting in the cooler months of spring or fall is ideal.
- Shade Cloth: If you’re growing lettuce in hotter climates, consider using shade cloth to prevent bolting and extend the growing season.
3. Culinary Uses of Lettuce Batavia Herb Seeds
- Flavor Profile: Batavia lettuce has a mild, slightly sweet flavor with a crisp texture. It’s less bitter than many other lettuce varieties, making it ideal for fresh salads and sandwiches.
- Uses:
- Salads: The crisp texture and wavy leaves of Batavia lettuce make it a perfect base for green salads. It pairs well with vinaigrettes and creamy dressings.
- Wraps: Batavia lettuce leaves are sturdy enough to be used as wraps, especially for low-carb or gluten-free dishes.
- Sandwiches: Use Batavia lettuce as a fresh, crunchy layer in sandwiches and burgers.
- Garnishes: Its attractive, wavy leaves can also be used as a garnish for dishes.
4. Nutritional Benefits of Lettuce Batavia Herb Seeds
- Vitamins and Minerals: Batavia lettuce is rich in vitamins A, C, and K, as well as folate. It also contains small amounts of iron and calcium.
- Low in Calories: Like most leafy greens, Batavia lettuce is low in calories, making it a healthy addition to any diet.
- Hydration: The high water content in lettuce helps keep you hydrated and supports overall digestive health.
5. Harvesting
- When to Harvest: Batavia lettuce can be harvested when the leaves are large enough to use, usually around 50–60 days after planting. It’s a loose-leaf variety, so you can begin harvesting outer leaves early and continue harvesting as the plant grows.
- How to Harvest: Snip or pinch off outer leaves at the base, leaving the center of the plant to continue growing. Alternatively, you can harvest the entire plant if you prefer.
- Continuous Harvesting: Lettuce is a “cut-and-come-again” crop, meaning that harvesting leaves encourages the plant to produce more.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.